Build custom delegate images with third-party tools
Harness Manager installs and configures delegates with the binaries that most CI/CD pipelines require. In some cases, however, a preconfigured image isn't the right fit. For example, preconfigured images can:
- Introduce the vulnerabilities of the binaries they include.
- Restrict you to the use of the included third-party tools and versions.
This document explains how you can:
- Build and host a custom delegate image that includes the tools you select.
- Use your custom delegate in CI/CD pipelines.
Delegates with an immutable image type (image tag yy.mm.xxxxx) include non-root user privileges and are compatible with OpenShift. For information on delegate types, go to Delegate image types.
About the Harness Delegate minimal image
Harness recommends that you use the Harness Delegate minimal image (yy.mm.xxxxx.minimal) when you set up the Harness Platform for production use. This image has been thoroughly scanned and is free of any high or critical vulnerabilities. Users focused on security tend to prefer this option.
However, the minimal delegate image lacks some binaries that are required for Continuous Delivery (CD) steps to function properly and remain vulnerability-free from third-party tools. Consequently, using the minimal delegate image requires you to configure your delegates and install necessary binaries. For information on delegate types, go to Delegate image types.
The Harness Delegate minimal image (yy.mm.xxxxx.minimal) is a lighter, more secure version of the default Harness Delegate image. Its main purpose is to provide an enhanced security profile for users, especially those who prioritize their systems' security. The Harness Delegate minimal images includes the following features.
-
Security Scanned: The image undergoes rigorous scanning processes to ensure that it is devoid of any high-risk or critical vulnerabilities. This makes it an optimal choice for organizations or users who have stringent security requirements. Harness aims to minimize critical/high vulnerabilities within this image. Achieving complete mitigation isn't always possible due to the continual discovery of vulnerabilities in third-party libraries/tools without immediate remediation.
-
Limited Binaries: Unlike the standard delegate, the minimal image does not include all of the default binaries. While this contributes to its lightweight nature and security, it also means that users have additional responsibilities. They must manually configure and add any necessary binaries to make their setup functional.
-
User Responsibilities: Because the minimal delegate image is devoid of the default binaries, users are in charge of tailoring it to their needs. This includes installing specific binaries essential for their CD steps. This level of control also allows users to maintain an updated environment. By installing the latest versions of necessary binaries, they can ensure that the delegate remains free from potential vulnerabilities found in outdated third-party tools.
-
Preferred by Security-Conscious Users: Due to its clean security slate, many users who prioritize system security gravitate towards the minimal delegate image. By starting with a minimal setup and adding only what is necessary, they can maintain a tighter control over the software and tools present, thus minimizing potential security risks.
Use the delegate minimal image to create a custom delegate image
Select the delegate minimal image
You can build on either of the following Harness-provided images.
| Image | Description |
|---|---|
| Harness Delegate Docker image | A publicly available Docker image providing Harness Delegate. |
| Harness Minimal Delegate Docker image | A minimal delegate image is available in Docker Hub at https://hub.docker.com/r/harness/delegate/tags. |
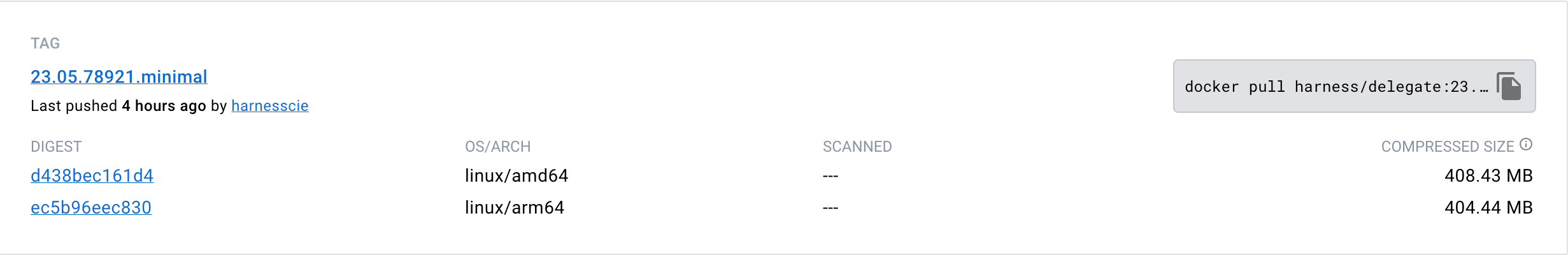
Use the last published yy.mm.xxxxx version of the minimal image from the Docker repository.
Build the delegate image
When you build a custom delegate image, you modify the image you select with user privileges and binaries. This section explains the build script used for the process. In this example, the script builds a custom image for deployment by Kubernetes and by Terraform.
The first lines of the script provide information about the base image and user privileges. This example uses the minimal image with delegate minor version 77029.
FROM harness/delegate:24.04.82804.minimal
USER root
The delegate container is granted root user privileges.
The first RUN block installs or updates the unzip and yum-utils tools. The --nodocs option prevents the installation of documentation on the image.
RUN microdnf update \
&& microdnf install --nodocs \
unzip \
yum-utils
The second RUN block uses the yum utility to create a configuration file for the HashiCorp repository, and then uses the microdnf package manager to install the required Terraform components:
RUN yum-config-manager --add-repo https://rpm.releases.hashicorp.com/RHEL/hashicorp.repo \
&& microdnf install -y terraform
The final RUN block retrieves the Kubernetes kubectl command-line tool that is required to manipulate clusters. The Linux chmod +x instruction makes the utility executable:
RUN mkdir /opt/harness-delegate/tools && cd /opt/harness-delegate/tools \
&& curl -LO "https://dl.k8s.io/release/$(curl> -L -s https://dl.k8s.io/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl" && chmod +x kubectl
The ENV instruction defines the Linux $PATH environment variable that provides the location of the tools to be installed:
ENV PATH=/opt/harness-delegate/tools/:$PATH
The final instruction switches the user back to harness to ensure the custom image does not run as root:
USER harness
The complete script is as follows:
FROM harness/delegate:24.04.82804.minimal
USER root
RUN microdnf update \
&& microdnf install --nodocs \
unzip \
yum-utils
RUN yum-config-manager --add-repo https://rpm.releases.hashicorp.com/RHEL/hashicorp.repo \
&& microdnf install -y terraform
RUN mkdir /opt/harness-delegate/tools && cd /opt/harness-delegate/tools \
&& curl -LO "https://dl.k8s.io/release/$(curl -L -s https://dl.k8s.io/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl" && chmod +x kubectl
ENV PATH=/opt/harness-delegate/tools/:$PATH
USER harness
The following example Dockerfile adds all the tools necessary for the Harness platform that are not part of the base image to the minimal delegate. You can remove tools for features you don't use or update versions for your requirements.
Example Dockerfile with all tools
Upload the image to Docker Hub
The next step is to upload your custom image to Docker Hub. For information on working with Docker repositories, go to Manage repositories in the Docker documentation.
Modify the delegate manifest
Before you can deploy a delegate, you must:
- Update the image path to the repository location of the custom image.
- Suspend delegate auto-upgrade functionality.
Delegate auto-upgrade is not compatible with custom images.
Example manifest file
Upgrade the image path
Open the delegate manifest file and locate the container spec (spec.containers). Change the image path to reflect the repository location of your uploaded image as shown in the following YAML.
spec:
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 600
restartPolicy: Always
containers:
- image: example/org:custom-delegate
imagePullPolicy: Always
name: delegate
securityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
runAsUser: 0
For purposes of this example, the image was uploaded to example/org:custom-delegate.
Suspend delegate auto-upgrade
Before you deploy a custom delegate, you must suspend its auto-upgrade functionality. This step prevents your image from being automatically upgraded and the installed binaries removed.
To suspend auto-upgrade, in the delegate manifest, locate the CronJob resource. In the resource spec, set the suspend field to true as shown in the following YAML:
apiVersion: batch/v1beta1
kind: CronJob
metadata:
labels:
harness.io/name: custom-del-upgrader-job
name: custom-del-upgrader-job
namespace: harness-delegate-ng
spec:
suspend: true
schedule: "0 */1 * * *"
concurrencyPolicy: Forbid
startingDeadlineSeconds: 20
Deploy the delegate
You can deploy the delegate from Harness Manager or by applying the modified delegate manifest file to your cluster.
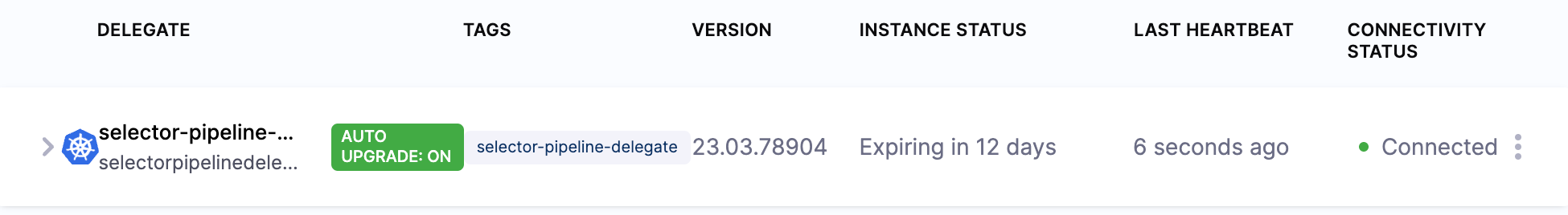
You can confirm the successful deployment and registration of the delegate in Harness Manager. Check the delegate information to ensure that auto-upgrade is not enabled.
Use your custom delegate image in pipelines
You can use your registered delegate to run Kubernetes and Terraform pipelines. It is a good idea to run a pipeline to validate the delegate image. Harness steps in your pipelines use the installed tooling on the delegate to perform builds or deployments.
For information about creating a Kubernetes pipeline, go to Kubernetes deployment tutorial.
For information about creating a Terraform Plan, go to Provision with the Terraform Apply Step.
